In the following lines, I will mention a simple summary about the topic of the systematic literature review. I quickly compiled this summary based on some sources for the benefit of those interested in this topic.
Systematic reviews have a long history. In the 18th century, Dr James Lind emphasized the importance of producing a comprehensive and unbiased critical overview of the existing literature on the treatment of scurvy (vitamin C deficiency). Other researchers followed up on some of the reviews published in the early 20th century, conducted in fields such as medicine, agriculture, physics, education and social sciences. In 1972, Archie Cochrane (a Scottish physician) published a textbook entitled Effectiveness and Efficiency: Randomized Reflections on the Health Service. Cochrane drew attention to the vital importance of randomized control trials in determining the effectiveness of health treatments. This led to an increased international focus on the need for improved research synthesis by policy makers, academics and clinicians. Gradually, the systematic review method was used in other fields outside health care as a way of summarizing current research in a comprehensive and systematic manner. By the late 20th century, it had become increasingly difficult for busy clinicians to know the best and most up-to-date evidence to guide practice. The problem was not only the sheer volume of literature but also the variable quality of reviews.
The stages of the development of the systematic review can be divided into: the founding period (1970-1989), the consolidation stage (1990-2000), and the diversification stage starting from 2001 onwards.
Many medical organizations around the world use the systematic review method, including the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE, UK), the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (USA), and the World Health Organization. Another prominent organization is the Cochrane Collaboration, a group of more than (13,000) volunteers with more than (50,000) contributors in more than (120) countries around the world. Volunteers specializing in health care conduct systematic reviews of medical scientific research and experiments, which facilitates the decision-making process by medical specialists, as well as patients and health policy makers. This organization was founded in (1993) and is headquartered in Oxford. In (2011), this organization signed an agreement with the World Health Organization to provide scientific data that establishes the organization’s decisions. The organization relies on the Cochrane Library, which includes a group of databases in medicine and health care, which in turn include systematic reviews and meta-analyses that summarize and interpret the results of medical research.

Structured reviews are also used in education, forensic science, social science, social welfare, international development, economics, environmental science, environmental health and toxicology: a branch of biology, chemistry, medicine and pharmacy, which studies the effects of chemicals on living organisms, especially humans. Toxicology studies the side effects of toxic chemicals, the symptoms they cause, the mechanisms that cause these symptoms, their treatment and how to detect these toxic substances. Structured reviews are a relatively recent innovation in the field of environmental health and toxicology. The first comprehensive frameworks for conducting structured reviews of environmental health evidence were issued in 2014 by the Office of Health Evaluation and Translation of the US Toxicology Program. The number of structured reviews has increased since then, until 2020, when the first general standard for structured reviews was established in the field of environmental health and toxicology. The following figure provides an overview of the structured review process:
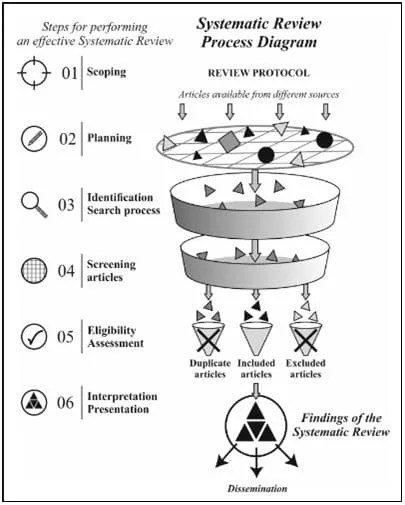
In 2019, a published study mentioned (15) tools used for structured review, including: (DistillerSR), (Swift Active Screener), (Covidence), (Rayyan), (Sysrev).
It is worth mentioning that systematic reviews involve a strict approach to collecting and synthesizing the literature under study. However, on the other hand, they face many limitations, the most important of which is the issue of bias that may result from the subjectivity of those conducting the systematic review, in addition to the issue of the time validity of the data collected, which often requires continuous updating for some specialties such as health care.

The following video provides an overview of how to conduct a structured literature review:
References
-Wikipedia: Citing many sources.
-Hong, Q.N., Pluye, P. (2018). Systematic reviews: A brief historical overview. Education for Information (Special Issue). DOI 10.3233/EFI-180219.
-Peričić, T. and Tanveer, S. (2019). Why systematic reviews matter: A brief history, overview and practical guide for authors. Elsevier.
-Purssell E., McCrae N. (2020) A Brief History of the Systematic Review. In: How to Perform a Systematic Literature Review. Springer, Cham.
-Koutsos, T. M., Menexes, G. C., & Dordas, C. A. (2019). An efficient framework for conducting systematic literature reviews in agricultural sciences. Science of The Total Environment, 682, 106-117.
-Youtube, Center for Evidence Synthesis in Health






